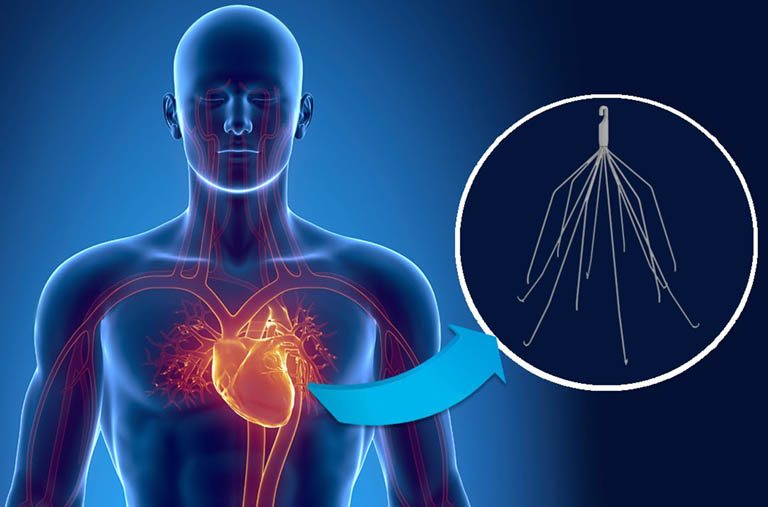
The IVC filter is a device intended to help prevent pulmonary embolism. It is an implanted filter that can also be used when other methods, such as anticoagulants and thrombolytics, fail to disperse an embolism. This article discusses the pros and cons of the IVC filter, how they work and how they are designed.
Blood clots can cause pulmonary embolism, a potentially life-threatening heart condition. If you have had a blood clot in the past, you might be at risk for one again. One way to prevent this is by wearing an IVC filter.
What is an IVC filter?
An IVC filter is a device that prevents blood clots. Clots can form in the inferior vena cava (IVC), which is a large vein that carries blood from the lower body to the heart. If a clot forms in the IVC, it can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism (PE).
An IVC filter is a device that prevents blood clots. It’s typically placed in the patient’s vein to reduce the risk of stroke or heart attack.
How does it help prevent a pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a potentially fatal complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when blood clots form in the deep veins of the legs and travel to the lungs. The most common causes of DVT are immobility, obesity and cancer surgery. About 75% of PE cases are caused by DVT, and about 25% are caused by other factors.
The risk of developing PE increases with age, obesity, smoking and previous episodes of DVT. Risk factors for developing DVT include: sitting for a long time; having long leg bones; being tall; having a family history of blood clots; being female; having diabetes mellitus; being overweight; undergoing surgery such as childbirth or an operation on the legs.
Most people who develop DVT don’t have any symptoms until the clots form in the deep veins and travel to the lungs. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, chest pain and coughing up blood.
If you have risk factors for developing DVT, it’s important to get checked regularly for signs and symptoms of PE. If you develop any signs or symptoms of PE, see your doctor immediately. Treatment includes stopping activity that has caused the DVT, taking anticoagulants (blood-thinning drugs) to prevent clotting and receiving pulmonary
Types of IVC Filters
There are three types of IVC filters: mechanical, heparin, and gelatin. Mechanical filters are the oldest type and use a mesh or fabric to trap clots. Heparin filters use anticoagulants to prevent clots from forming. Gelatin filters are newer and use a polymer network to absorb blood proteins and collagen.
There are different types of IVC filters designed to prevent blood clots. One type is the heparin filter, which uses a synthetic antibody to attach to platelet receptors on the surface of the red blood cells. This blocks them from forming clumps, which can lead to a stroke.
A second type of IVC filter is the anticoagulant filter. This uses a substance that stops the blood from clotting, either by breaking down the blood clots or stopping their growth. The most common anticoagulant used in IVC filters is heparin.
There are a few types of IVC filters: heparin, anti-coagulant, and thrombin inhibitors. Heparin is the most common type of filter and it prevents blood clots by stopping the formation of blood clots. Anti-coagulant filters work by preventing the clotting of blood by inhibiting different enzymes. Thrombin inhibitors work in the same way as anti-coagulants but they also inhibit thrombin from forming clots.
Side Effects of an IVC Filter
One of the most common side effects of an IVC filter is temporary pain and discomfort. This can occur due to the device placement or because of inflammation around the filter site. Other side effects that can occur include infection, fluid accumulation around the filter, or device removal because of a complication.
If any of these side effects persist or become bothersome, it is important to seek medical attention.
Conclusion
As we age, our risk of developing blood clots increases. This is because as we age, the ability of our blood to clot diminishes. If you are at risk for developing blood clots, an IVC filter can help prevent them from occurring.
There are a few things you should keep in mind when considering whether or not to get an IVC filter: first and foremost, it is important to talk with your doctor about your individual risks. Secondly, make sure to research which type of IVC filter is right for you; there are a number of different types available on the market today. And finally, be patient – it may take some time before your device becomes effective at preventing blood clots.
A device that prevents blood clots is an important part of any health care regimen. Unfortunately, sometimes people can develop blood clots in the veins near the heart. If this happens, the IVC filter can help prevent the clot from traveling to the heart and causing a stroke or other serious medical issue. So if you are at risk for developing blood clots, it is important to talk to your doctor about whether or not an IVC filter may be right for you.








Leave a Reply